

Energy intensity is an indication of how much energy is used to produce one unit of economic output. For every unit reduction (in L / person / day ) of indoor residential water use, it is estimated that up to 225 MWh may be saved annually. Energy intensity level of primary energy (MJ/2011 USD PPP): A ratio between energy supply and gross domestic product measured at purchasing power parity. In 2007, APEC Leaders proposed a regional goal to reduce energy intensity by at. It is found that the residential sector in the city can have the greatest impact in affecting energy requirements associated with water use. APEC Economies consume approximately 60 percent of the worlds energy. The energy intensity is estimated at an electricity consumption of 4380. The dominant use of energy in this segment is attributed to water heating requirements, and the total energy use for obtaining hot water is estimated to range from approximately 20 to 50 million kWh annually. Excluding natural gas use for feedstocks the primary energy consumption is. Results show that the energy intensity (in electric kWh) in WES for Masdar City may range from 2.6 to 4 kWh / m 3. The framework is applied to Masdar City, a new urban area in the United Arab Emirates, which has been targeted in its design to be a future zero-carbon and zero-waste city.

Low energy intensity indicates a lower price or cost of converting energy into GDP. High energy intensities indicate a high price or cost of converting energy into GDP. It is calculated as units of energy per unit of GDP.
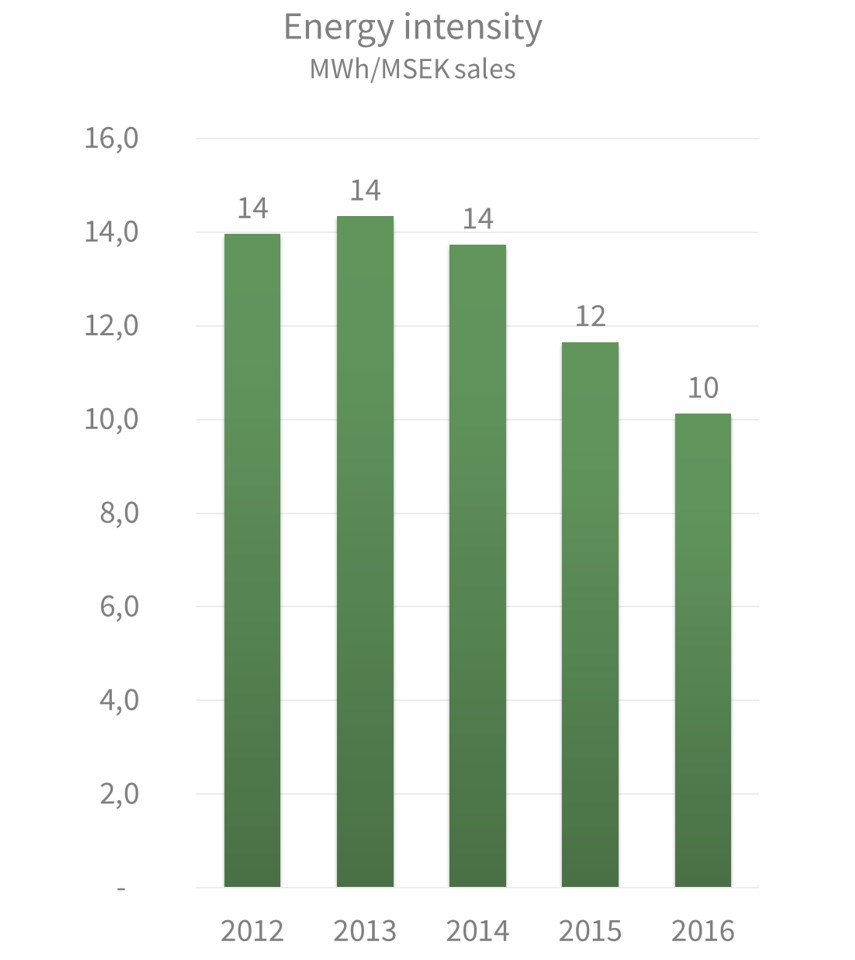
In this paper, an analytical framework is presented which can be used at the planning stages of new urban developments to assess future building-level water demands and associated energy requirements. The World Bank : PPP per kg of oil equivalent (2011) Energy intensity is a measure of the energy inefficiency of an economy. The water end-use segment (WES), consisting of activities that utilize water in homes and buildings, has been identified as a major component of energy use in the urban water supply system. Through partnership with Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) and East Bay Municipal Utility District (EBMUD) we have established a basic method for assessing the energy intensity of water delivery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
